Male Pattern Balding: Causes, Stages, and Signs of Hair Loss
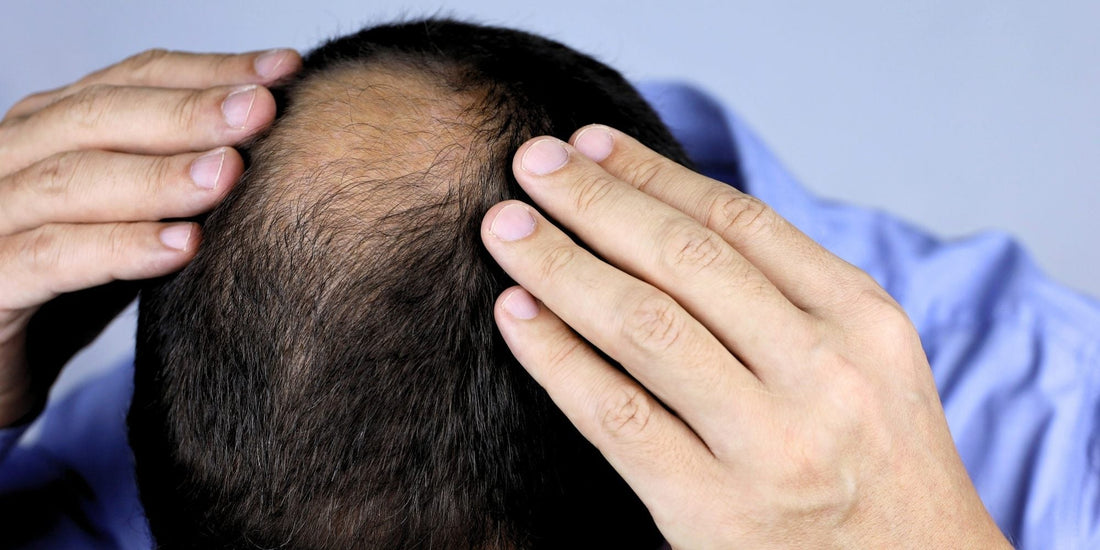
Male pattern balding is a common form of hair loss that often starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown. Over time, it can progress to significant baldness. Understanding its causes, stages, and treatments can help manage hair loss effectively.
This guide covers the stages of baldness, the possibility of regrowth, and the best treatment options available today. Whether you're noticing early signs or advanced thinning, this article will help you take control of your hair health.
What Age Do Men Start Balding?
Male pattern balding often begins in a man's 30s, but it can start as early as the late teenage years or early 20s. Hair loss is a gradual process, and many men notice the first signs, such as a receding hairline or thinning at the crown, before turning 40. By the age of 50, over 50% of men experience some degree of baldness.
Genetics plays a significant role in determining when and how quickly hair loss progresses. If male relatives have experienced early hair loss, there's a higher chance of developing it at a younger age.
Why do Men go Bald?
Male pattern balding, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is caused by a combination of genetics and hormones. The primary factor is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone that affects hair follicles.
How DHT Affects Hair Follicles:
DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time. This process, known as follicular miniaturization, leads to:
- Shorter hair growth cycles – Hair falls out faster than it can grow.
- Thinner, weaker strands – Hair becomes finer before eventually stopping growth.
- Permanent follicle inactivity – Once a follicle stops producing hair, regrowth becomes nearly impossible.
Hormonal imbalances, stress, poor diet, and medical conditions can contribute to hair loss, but genetics remain the most significant factor.
Receding Hairline Stages:
A receding hairline follows a predictable pattern, usually classified using the Norwood Scale. This scale helps track the progression of male pattern balding from early signs to complete hair loss.
Stage 1: No Visible Hair Loss
At this stage, the hairline remains full, and there are no signs of thinning or recession. Most men in their teens or early 20s fall into this category.

Stage 2: Slight Recession
A small amount of hair loss occurs at the temples, creating a mild "M" shape. This is often the first noticeable sign of hair loss but may not be obvious unless closely examined.

Stage 3: Deeper Recession
Hairline recession becomes more pronounced, and the "M" shape is more visible. Some men may also start experiencing thinning at the crown, although it's usually mild at this stage.

Stage 4: Noticeable Hair Loss at the Crown and Temples
The hairline continues to recede, moving further back on the forehead. At the same time, thinning at the crown (top of the head) becomes more evident. However, a band of hair still separates the balding areas.

Stage 5: Widening Bald Spots
At this stage, hair loss at the temples and crown becomes more severe. The strip of hair separating them is still there but much thinner. The head begins to take on a horseshoe-shaped pattern of remaining hair.

Stage 6: Merging Bald Areas
The bridge of hair between the receding hairline and the bald crown disappears, leaving one large balding region. The remaining hair on the sides and back of the head is still thick but may start thinning.

Stage 7: Complete Baldness
The final stage of male pattern balding leaves only a thin ring of hair around the back and sides of the scalp. Most of the top of the head is completely bald. At this point, hair loss is permanent, and regrowth is unlikely.

Signs of Alopecia:
Alopecia is a medical term for hair loss, and it can affect the scalp or other parts of the body. While male pattern balding is a form of androgenetic alopecia, other types exist, such as alopecia areata (an autoimmune disorder).
How Alopecia Affects the Body:
Depending on the type, alopecia can cause:
- Patchy or complete hair loss on the scalp.
- Thinning or shedding of eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
- Scalp irritation, redness, or discomfort in some cases.
Alopecia affects people differently, but in most cases, the impact is cosmetic rather than physical. However, hair loss can significantly affect self-esteem and confidence.
The symptoms of alopecia vary based on the type and severity of hair loss. Some common signs include:
- Gradual thinning on the top of the head – The most common pattern in male baldness.
- Circular or patchy bald spots – Often seen in alopecia areata.
- Sudden hair shedding – Stress, illness, or medical treatments may cause excessive hair fall.
- Widening part line – A sign of thinning hair before visible bald patches appear.
If hair loss progresses quickly or comes with scalp irritation, consulting a doctor or dermatologist is recommended.
Male Pattern Baldness Stages:
Male pattern balding and a receding hairline are often confused, but they are not the same. While a receding hairline is usually an early sign of male pattern baldness, not everyone with a receding hairline will go completely bald. Understanding the key differences can help determine the best course of action for hair loss management.
What Is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline occurs when the hair at the temples gradually moves backward, forming an "M" or "V" shape. This process can start as early as the late teens or early 20s.
Key Features of a Receding Hairline:
- Hairline moves backward from the forehead.
- Often forms an M-shaped pattern at the temples.
- Can remain stable for years without progressing to full baldness.
- Hair on the crown may remain thick and unaffected.
A receding hairline can be caused by genetics, aging, stress, or even excessive hairstyling. However, a receding hairline alone does not always indicate male pattern baldness. Some men experience a mild recession that never develops into significant baldness.
How Male Pattern Balding Differs:
Male pattern baldness is a more advanced and progressive condition that follows a predictable Norwood Scale pattern. It often starts with a receding hairline but eventually leads to thinning at the crown and complete hair loss on the top of the head.
Key Features of Male Pattern Balding:
- Begins with a receding hairline but progresses to thinning at the crown.
- Hair loss follows a specific pattern, eventually leading to a horseshoe-shaped hairline.
- Caused primarily by genetics and DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which shrinks hair follicles over time.
- It can result in complete baldness on the top of the head if untreated.
Receding Hairline vs. Male Pattern Balding:

Can Male Pattern Baldness Regrow?
While male pattern baldness is largely genetic and progressive, there are some ways to slow, stop, or even reverse hair loss if treated early. However, once the follicles have completely stopped producing hair, regrowth becomes much more difficult.
Ways Hair Can Regrow:
- Medications (FDA-approved treatments) – These can help slow hair loss and stimulate regrowth.
- Hair Transplants – This procedure moves healthy hair follicles to balding areas.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) – Stimulates hair follicles to promote growth.
- Lifestyle and Diet Improvements – Proper nutrition can support hair health.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy – Uses the body’s own platelets to boost hair growth.
Men's Hair Loss Treatment:
There are several effective hair loss treatments available. Here’s a breakdown of the most common ones and how they work:
1. Minoxidil (Rogaine)
- How It Works: Increases blood flow to hair follicles, prolonging the growth phase of hair.
- Application: Applied directly to the scalp as a liquid or foam.
- Effectiveness: Works best for slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth, especially at the crown.
2. Finasteride (Propecia)
- How It Works: Blocks dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles.
- Application: Taken as a daily oral pill.
- Effectiveness: Helps maintain existing hair and may regrow some lost hair.
3. Hair Transplant Surgery
- How It Works: Healthy hair follicles from the back of the scalp are transplanted to bald areas.
-
Procedure Types:
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) – Individual follicles are moved.
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) – A strip of scalp with hair follicles is transplanted.
- Effectiveness: Provides permanent, natural-looking results but requires surgery.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- How It Works: A small amount of the patient’s blood is drawn, processed, and injected into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
- Effectiveness: This can improve hair thickness and regrowth, especially when combined with other treatments.
5. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- How It Works: Uses red light wavelengths to stimulate hair follicles and increase growth.
- Effectiveness: Helps slow hair loss and may promote regrowth when used consistently.
6. Hair Loss Shampoos & Topical Treatments
- How They Work: Contain ingredients like ketoconazole, biotin, and caffeine to support scalp health and reduce DHT levels.
- Effectiveness: Best for preventing hair loss rather than reversing it.
7. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
- How It Works: A cosmetic tattooing technique that creates the illusion of a shaved head or thicker hair.
- Effectiveness: It doesn’t regrow hair, but provides a natural-looking hairline for men with advanced baldness.
8. Wigs, Hairpieces, and Concealers
- How They Work: Non-medical options that provide immediate coverage for bald spots.
- Effectiveness: Aesthetic solution rather than a treatment.
Male pattern balding follows a predictable pattern, but treatments like medications, transplants, and laser therapy can slow or even reverse hair loss. Acting early increases the chances of preserving hair. Understanding your options is the first step toward managing baldness effectively.
Please note that the content provided in this blog post is intended for entertainment and informational purposes only. It should not be considered medical advice or a substitute for professional medical consultation, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog.
Upgrade Your Comfort with TBô Men’s Bamboo Underwear:
Experience the perfect blend of comfort and performance with TBô Men’s Bamboo Underwear. Designed for men who value quality, our underwear features moisture wicking and breathable fabric to keep you cool and dry all day. The antibacterial properties help prevent odor, while our man shaped pouch offers unmatched support and comfort. Plus, made from sustainable bamboo, TBô underwear is better for you and the planet.
Upgrade your everyday essentials with underwear that moves with you. Shop now and feel the TBô difference!