
The Biology of Male Arousal: What Really Happens in the Body?
Understanding male arousal goes beyond simple attraction or physical touch. It's a complex dance between hormones, the nervous system, blood flow, and the brain. In this blog, we break down exactly what happens during male arousal, from the first flicker of desire to full physiological response.
What is Male Arousal?
Male arousal is a complex process involving the brain, hormones, nervous system, and blood flow.
It begins with mental or physical stimulation, triggering the brain to release chemicals like dopamine and testosterone that increase sexual desire. These signals activate the nervous system, relax blood vessels, and direct blood flow to the penis, resulting in an erection.
Male arousal is influenced by both biological and psychological factors, including mood, confidence, and stress levels. Understanding how male arousal works can improve sexual health, enhance relationships, and help address issues like low libido or erectile dysfunction.

The Brain’s Role in Arousal
Arousal begins in the brain. Specifically, the hypothalamus plays a central role by activating hormones and neurotransmitters that kickstart the process. Dopamine, the pleasure chemical, is released in response to sexual stimuli—creating that unmistakable feeling of desire.
Other brain chemicals like oxytocin and serotonin help regulate mood and bonding, further enhancing the arousal experience. Mental stimulation, emotional connection, and fantasy all originate here.
Hormones Behind the Heat: Testosterone and More
Testosterone is often called the "sex hormone" for a reason. It significantly impacts libido and plays a vital role in male sexual function. But it’s not alone. Cortisol (the stress hormone), oxytocin, and vasopressin all interact in the arousal process.
Low testosterone can contribute to reduced libido, difficulty achieving an erection, and low energy. Understanding this hormonal symphony helps answer the question, "How does testosterone affect arousal?"
Nervous System Activation: Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
Two branches of the autonomic nervous system work in balance during arousal:
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Activated during relaxation, it enables blood to flow to the penis, initiating an erection.
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Kicks in during the climax or during stress, leading to ejaculation or interruption of arousal.
Stress can disrupt this balance, leading to issues like performance anxiety or erectile dysfunction.
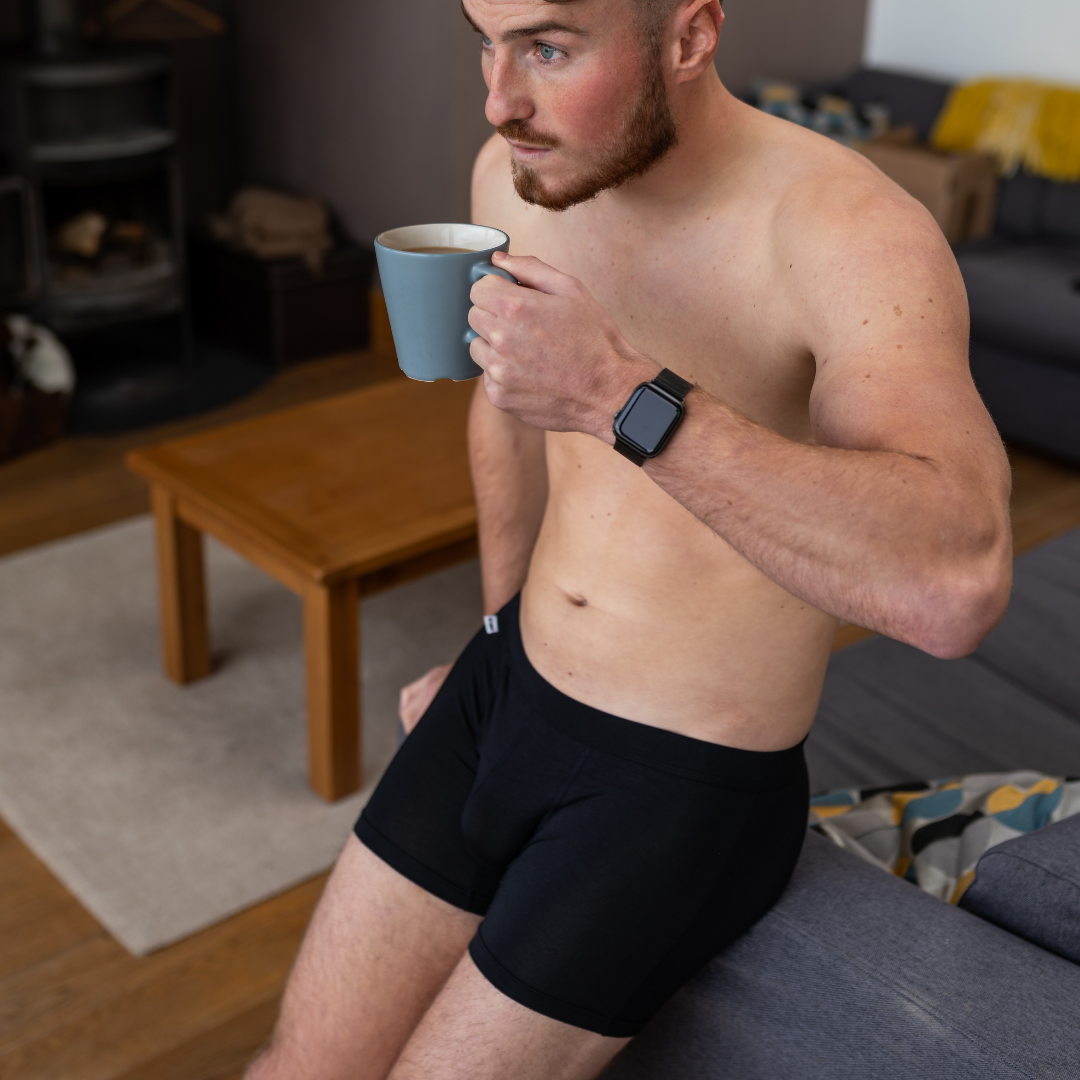
How Male Underwear Can Affect Male Arousal
Male underwear isn’t just about comfort or support—it can also influence arousal, both physically and psychologically. The type, fit, fabric, and design of underwear can impact sensitivity, confidence, and even hormone regulation, making it more relevant to male arousal than most people think.
Tight-fitting underwear, for example, can restrict blood flow and increase heat around the genitals, potentially lowering testosterone levels over time. Since testosterone plays a major role in male libido and sexual function, this can affect the arousal process. Breathable fabrics like bamboo or cotton help regulate temperature, protect sperm health, and support healthy circulation—all of which contribute to better sexual wellness.
From a psychological perspective, the right underwear can boost body confidence. Feeling attractive in your underwear may increase self-esteem and mental readiness for intimacy. This is especially true with underwear designed to enhance or contour the male package, which may trigger visual and tactile arousal cues for both the wearer and their partner.
Certain materials—like Bamboo, mesh, or modal—add to the sensory experience, increasing physical stimulation. Underwear that fits well and feels good can activate tactile receptors in the skin, contributing to the early stages of arousal.
In short, male underwear can support or hinder sexual readiness based on its design and feel. Choosing the right pair doesn’t just affect daily comfort—it may actually play a subtle yet meaningful role in the biology of male arousal.
The Erection Process: Blood Flow and Physiology
Erections happen when the brain sends signals to relax the muscles in the penis. This allows blood to rush into two sponge-like regions called the corpus cavernosum. The presence of nitric oxide helps dilate blood vessels, sustaining the erection.
This is a textbook example of how closely arousal is linked to vascular health. Conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes can interfere with this process, highlighting the importance of overall wellness.
External Triggers and Sensory Input
What triggers male arousal? Sensory stimulation is key:
- Visual: Erotic images or body language
- Tactile: Touch, massage, or pressure
- Auditory: Erotic talk, music, or breath
These inputs stimulate the brain and start the arousal loop. For many, mental stimulation and emotional intimacy are just as powerful.
The Phases of Male Sexual Response
There are four main stages of male arousal:
1. Excitement: Triggered by stimuli and hormone release
2. Plateau: Heightened tension and blood flow
3. Orgasm: Ejaculation and rhythmic muscle contractions
4. Resolution: Return to resting state
This arousal cycle varies by individual and is influenced by age, health, and psychological factors.
Common Issues: When Arousal Doesn’t Work as Expected
Many men experience issues with arousal at some point. Common causes include:
- Low testosterone
- Performance anxiety
- Chronic stress
- Medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart disease)
Treatments can range from lifestyle changes to therapy and medication. Boosting male libido naturally may involve exercise, a healthy diet, and stress reduction techniques.
Conclusion
Male arousal is a highly coordinated effort between the mind and body. From brain chemistry to blood flow and hormones, it’s a finely tuned process that deserves greater understanding. The more we know, the more we can support sexual health in men.
Whether you're looking to improve your own sexual function or support a partner, understanding the biology of male arousal is a key step.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What hormones are involved in male arousal?
Testosterone, oxytocin, vasopressin, cortisol, and dopamine are all involved. These hormones help regulate libido, bonding, and stress levels.
How does the brain contribute to sexual arousal?
The brain, especially the hypothalamus, releases dopamine and activates nerve responses that trigger arousal. Mental stimulation and fantasy also play a role.
What causes low libido in men?
Common causes include low testosterone, high stress, sleep issues, and underlying health problems. Psychological factors like depression can also contribute.
How does blood flow impact erections?
An erection is caused by increased blood flow to the penis. Nitric oxide helps dilate blood vessels, allowing blood to enter and stay in the corpus cavernosum.
What are the stages of male arousal?
Excitement, Plateau, Orgasm, and Resolution. These stages are driven by hormones, nerve responses, and muscle contractions.
Can stress affect male arousal?
Yes, chronic stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, which can inhibit erections and decrease libido.










1 comment
Thanks for the Info